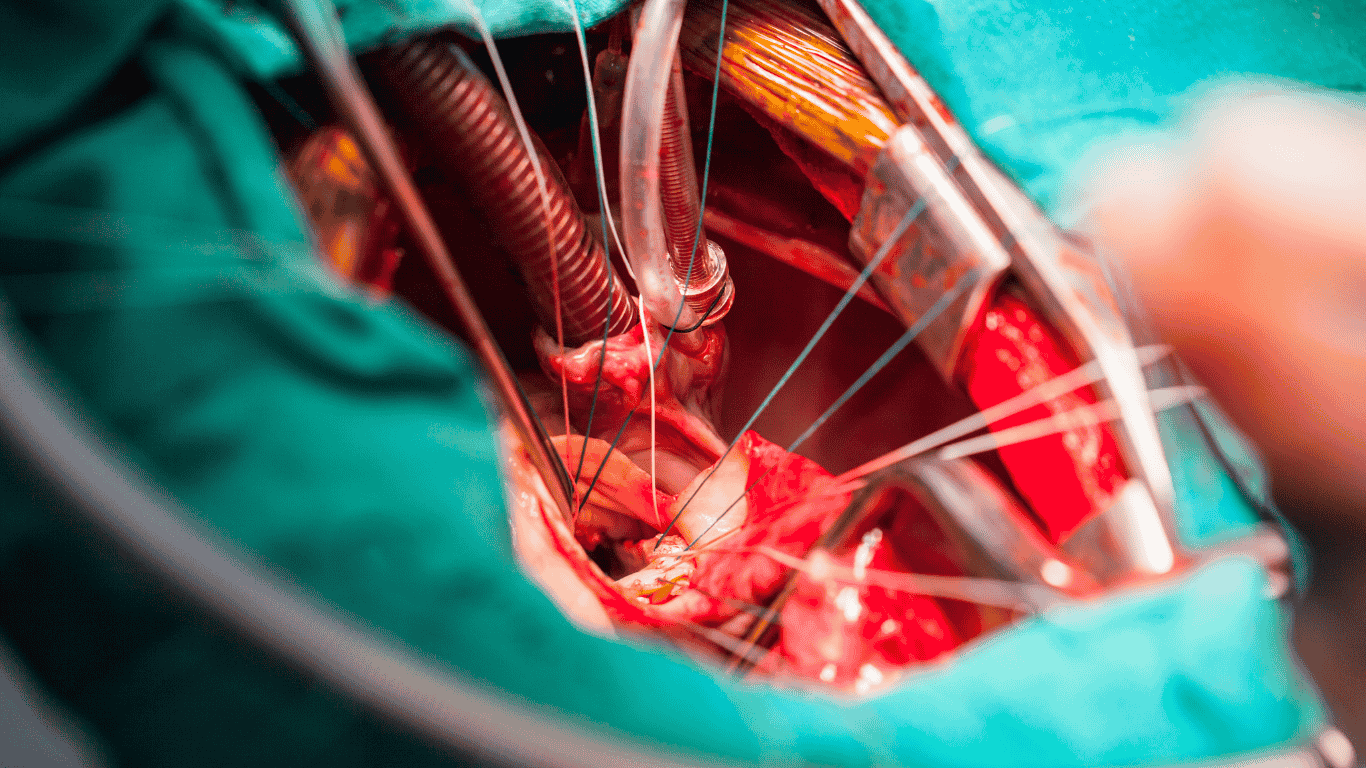
Three TAVR Surgeries in a Row Signal Shift in City’s Cardiac Care
Nagpur is emerging as a hub for advanced cardiac care, as a leading hospital in the city recently completed a “hat-trick” of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) procedures. This minimally invasive treatment, which replaces a narrowed aortic valve without open-heart surgery, is gaining popularity among patients who are high-risk or not ideal candidates for conventional valve replacement.
What is TAVR?
TAVR is a revolutionary heart procedure that allows doctors to replace a damaged aortic valve using a catheter, usually inserted through the leg. The valve is expanded inside the existing valve, restoring blood flow and significantly improving patient outcomes, especially among the elderly or those with other health complications.
Who Benefitted?
The three patients who underwent the procedure were all elderly individuals suffering from severe aortic stenosis—a condition where the heart’s aortic valve narrows, reducing blood flow and increasing the risk of heart failure. All three had other comorbidities, making them unsuitable for traditional surgery.
Dr. Sameer Arbat, a noted interventional pulmonologist, and Dr. Amogh Baste, a structural heart disease specialist, led the team that successfully performed the surgeries.
“These successful cases mark an important milestone in Nagpur’s journey toward adopting global best practices in cardiac intervention,” said Dr. Baste.
A Sign of Changing Times in Cardiac Health
This hat-trick of procedures indicates a growing trust in minimally invasive heart treatments and increased awareness among patients. Hospitals in tier-2 cities like Nagpur are now equipped with advanced technologies, experienced teams, and specialized infrastructure that were once limited to metro cities.
The procedures were performed at Getwell Hospital, which has been steadily building its reputation for complex heart and lung interventions.
Why It Matters
India’s burden of cardiovascular diseases is among the highest globally. Procedures like TAVR offer safer, faster, and more cost-effective alternatives, particularly for the aging population. The success of such surgeries in Nagpur signals a broader trend of healthcare decentralization—bringing world-class treatment closer to regional populations.